
Blog
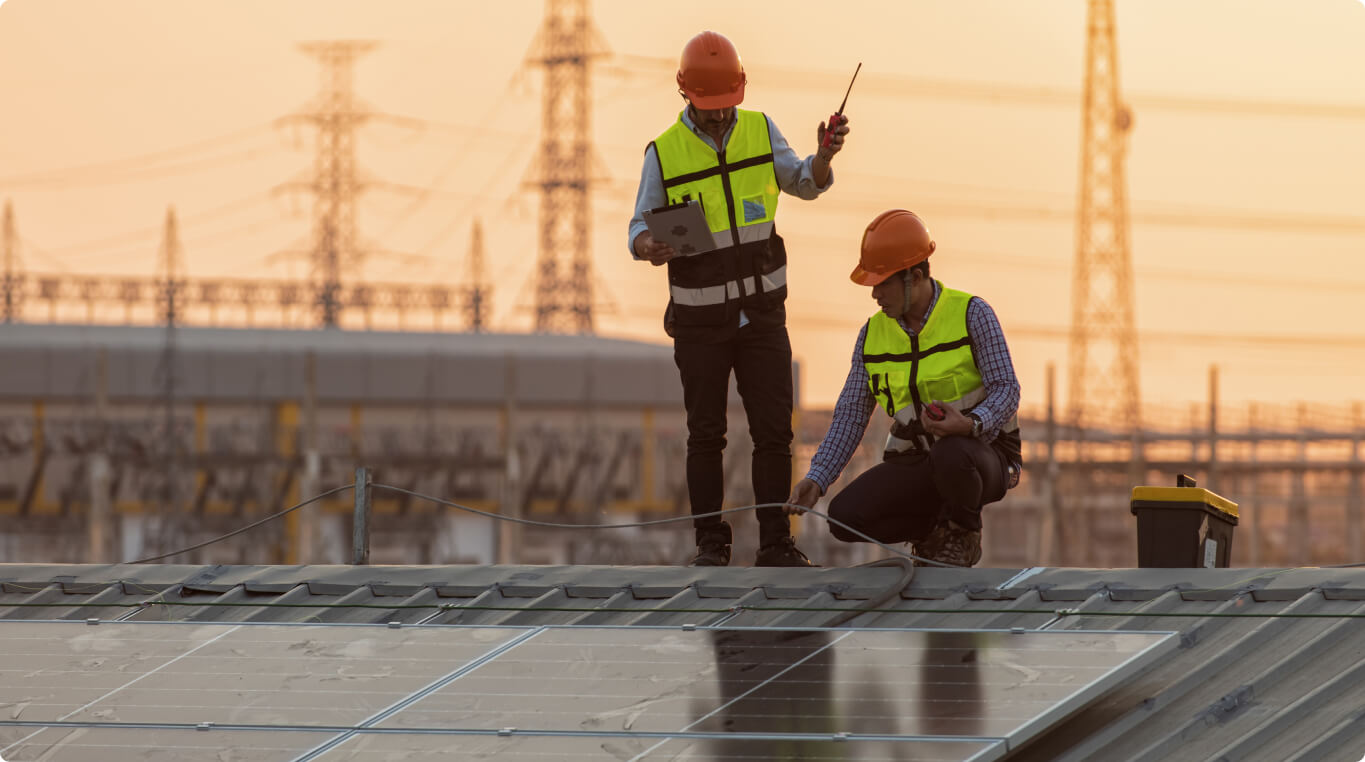

In recent years, India has made significant strides in promoting renewable energy, particularly through the grid connected rooftop solar programme. This initiative, launched by the Government of India, aims to harness solar power by encouraging residential, commercial, and industrial establishments to install rooftop solar panels.
Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Programme Overview
The Rooftop Solar Programme that connected consumers with the existing power grid, was initiated to meet the country’s energy demands sustainably. It allows consumers to generate their electricity using solar panels installed on rooftops and feed excess power into the grid. This not only reduces dependency on conventional energy sources but also promotes cleaner energy production.
Key Components and Benefits
Under this programme, consumers are eligible for subsidies and incentives to offset the initial installation costs of rooftop solar systems. The government provides financial support through various schemes, including the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana 2024, which aims to provide free electricity to eligible households by harnessing solar energy.
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana 2024
The PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana 2024 is a crucial component of the Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Programme. It targets rural and urban households, enabling them to install solar panels at no upfront cost. Beneficiaries not only receive free electricity but also contribute to reducing carbon emissions and fostering energy independence.
Implementation and Progress
Since its inception, the rooftop solar programme has seen widespread adoption across various states in India. State governments play a pivotal role in implementing and promoting rooftop solar installations by facilitating approvals, providing subsidies, and ensuring grid connectivity. This decentralized approach empowers local communities to embrace renewable energy solutions.
Policy Framework and Incentives
The policy framework supporting the Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Programme emphasizes net metering, which allows consumers to sell surplus electricity back to the grid. This encourages investment in solar power generation while ensuring economic viability for consumers. Additionally, accelerated depreciation benefits and tax incentives further enhance the attractiveness of rooftop solar investments.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its successes, the programme faces challenges such as financing constraints, technical complexities, and regulatory hurdles. Addressing these issues requires continued collaboration between policymakers, industry stakeholders, and financial institutions. Moreover, enhancing public awareness and capacity building are essential for scaling up rooftop solar installations.
Conclusion
India’s Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Programme represents a significant stride towards sustainable energy development. By leveraging solar power, the country aims to meet its energy demands efficiently while mitigating environmental impact. The PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana 2024 underscores the government’s commitment to providing clean and affordable electricity to all. As the programme evolves, fostering innovation and addressing implementation challenges will be critical in achieving India’s renewable energy targets.
In summary, the rooftop solar industry stands as an integral part of India’s vision for Aatmanirbhar Bharat and the programme works as a beacon of India’s commitment to renewable energy transition, offering tangible benefits to consumers, businesses, and the environment alike.